Energy production from waste
Waste is known as one of the major environmental and economic challenges in the world today. With the increase in population and industrial development, the production of waste has also increased dramatically. Proper waste management and using them to produce energy can help reduce pollution and preserve natural resources. Here we will examine the types of waste and different methods of producing energy from them.
Types of waste
Waste is generally divided into four main categories:
- Normal or dry waste: This type of waste includes household waste such as plastic, paper, metal and organic packaging.
- Hazardous waste: includes chemical, flammable and sharp materials that require special management.
- Medical waste: This type of waste is produced from medical and treatment centers and may contain infectious materials.
- Electronic waste: includes electronic and electrical devices such as televisions, computers and mobile phones.


Methods of producing energy from waste
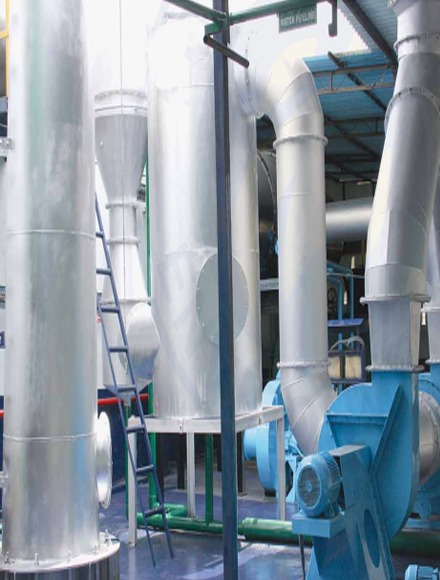

01
Garbage Burning
Waste incineration is one of the most common ways to generate energy from waste. In this method, waste is burned at high temperatures and the thermal energy produced is converted into electricity. This method helps to reduce the amount of waste, but it may cause the production of greenhouse gases.
The main components of the waste incinerator power plant:
- Waste storage: A place to store and prepare waste before incineration.
- Furnace: Where waste is burned at high temperatures.
- Boiler: turns the steam produced from the heat of the furnace into energy.
- Scrubber: to remove gaseous pollutants from exhaust smoke.
- Filter: To remove suspended particles from smoke.
- Chimney: To discharge refined smoke into the air.
- Water-steam path: including the steam cycle of the power plant to produce energy.
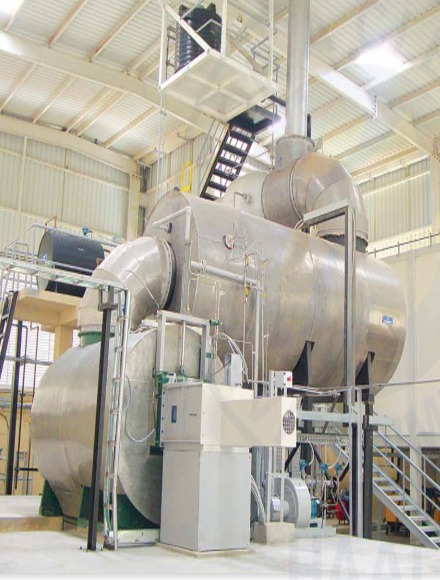

Waste incineration process:
- Collection and storage: Garbage is collected and stored in storage.
- Incineration: Waste is burned in a high-temperature furnace.
- Steam generation: The heat generated from burning waste is used to generate steam.
- Energy production: the produced steam is transferred to turbines and electrical energy is produced.
- Smoke purification: The smoke produced from the burning process is purified through scrubbers and filters to remove pollutants.
Advantages of waste incinerators
- Reducing the volume of waste: incineration can reduce the volume of waste by 95-96%.
- Energy production: This method can help produce electricity and heat.
- Eliminate toxic substances: Incineration can eliminate toxic and infectious substances.
- Reducing the amount of waste and eliminating toxic and infectious substances.
- Production of electricity and heat that can help reduce energy costs.
Disadvantages of incinerators
- Air pollution: This method may produce greenhouse gases and air pollutants.
- High cost: pollution control equipment and turbine cooling are expensive.
- Production of greenhouse gases and air pollutants that can lead to air pollution and climate change.
- High costs of equipment and maintenance of pollution control systems.
Sweden is one of the leading countries in the field of waste incineration. The country recycles or converts more than 99% of its waste into energy. Waste incineration plants in Sweden not only manage domestic waste, but also convert waste imported from other countries into energy.
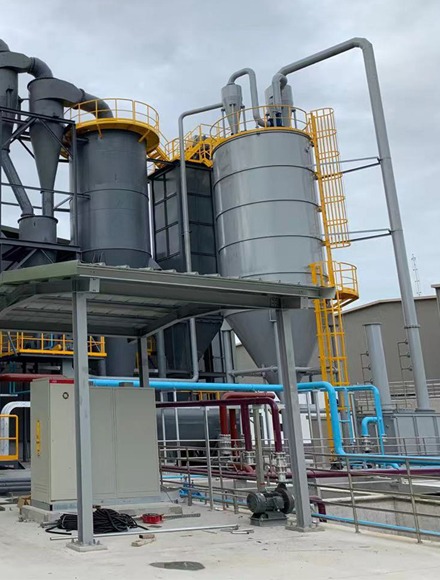

02
Biogas Production
Biogas production from organic waste is another effective method in waste management. In this process, organic residues are decomposed under anaerobic conditions and methane gas is produced. This gas can be used as fuel to produce electricity and heat.
Biogas is a renewable energy source that is produced from the decomposition of organic materials such as animal manure, food waste and sewage. This process is done anaerobically (without the presence of oxygen) and results in the production of methane gas, which is flammable.
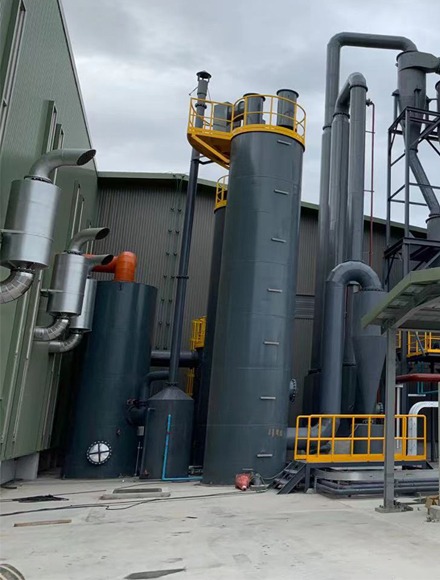

The main components of a biogas production system:
- Fermentation Tank: Where organic matter decomposes.
- Gas tank: to store the produced biogas.
- Purification system: To remove impurities and pollutants from biogas.
- Usage system: to use biogas as fuel or electricity generation.
Stages of biogas production:
- Hydrolysis: complex organic substances are converted into simpler compounds.
- Acidification: Simpler compounds are converted into organic acids.
- Gas production: organic acids are converted into methane and carbon dioxide.
- Purification: The produced gas is purified to remove impurities.
Advantages of Biogas
- Use of organic waste: This method uses organic waste such as food and agricultural waste.
- Production of clean energy: the produced biogas can be used as a clean fuel to produce electricity and heat.
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: This method can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and using organic waste that helps reduce environmental pollution.
- Production of clean fuel and reduction of energy costs.
Disadvantages of Biogas
- The need for a lot of space: for the production of biogas, a lot of space is needed for the anaerobic digestion of waste.
- Time-consuming: The biogas production process may be time-consuming.
- Initial costs: Installation and operation of biogas production systems is costly.
- Need for management: Biogas production systems need careful management and maintenance.
- The need for a lot of space for anaerobic digestion and proper management of the remaining waste.
- High initial costs for the construction and maintenance of biogas production units.
Germany is one of the most successful countries in biogas production. The country has more than 9,000 biogas production units that use agricultural waste, food waste, and urban sewage to produce biogas. The biogas produced in these units is used as fuel to produce electricity and heat.

03
Production of fuel derived from waste (RDF)
In this method, wastes are converted into solid fuels that can be used in power plants to generate electricity. This method helps to reduce the volume of waste and optimal use of resources.
Residue-derived fuel (RDF) is an alternative fuel produced from municipal solid waste. This fuel is prepared from combustible components of waste and can be used as a substitute for fossil fuels in some industries.
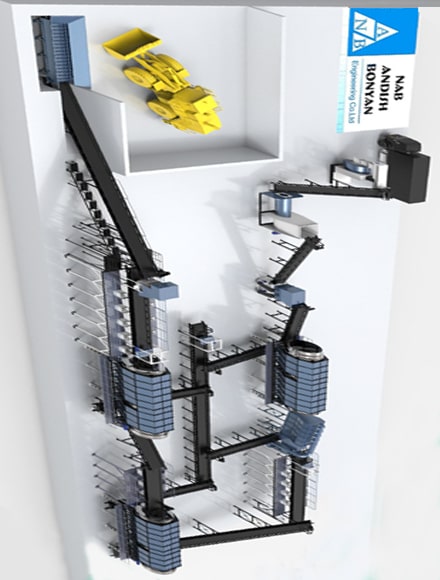
The main components of the RDF production process:
- Collection and separation: waste is collected and transferred to separation centers. In this step, recyclable and non-combustible materials are separated.
- Shredding: Segregated waste is crushed into smaller pieces to make the processing process easier.
- Drying: The moisture content of waste is reduced to increase its calorific value.
- Compression: Shredded and dried waste is compressed into pellets or briquettes to make them easier to transport and use.
Applications:
- Cement industry: RDF is used as an alternative fuel in cement kilns.
- Power plants: RDF can be used as fuel in power plants.
- Other industries: Some other industries can also use RDF as an alternative fuel.
Advantages of RDF
- Reducing the volume of waste: This method helps to reduce the volume of waste.
- Reducing the volume of waste: RDF helps reduce the volume of landfilled waste.
- Energy production: RDF can be used as fuel in power plants and various industries.
- Reduction of fossil fuel consumption: The use of RDF helps to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Reducing the volume of waste and reducing the need to bury waste, which helps to reduce soil and water pollution.
- Optimum use of resources and reduction of waste disposal costs.
Disadvantages of RDF
- Variable fuel quality: The quality of produced fuel may be variable and require further processing.
- Production costs: RDF production process requires advanced equipment and technologies, which is costly.
- Air Pollutants: Burning RDF can produce air pollutants that require careful control.
- The variable quality of produced fuel and the need for further processing that may lead to environmental pollution.
Processing costs and the need for advanced technologies to produce high quality fuel.
Japan is one of the leading countries in the use of RDF. Using advanced technologies, this country converts municipal waste into solid fuels that are used in power plants to generate electricity. This method helps to reduce the volume of waste and optimal use of resources.
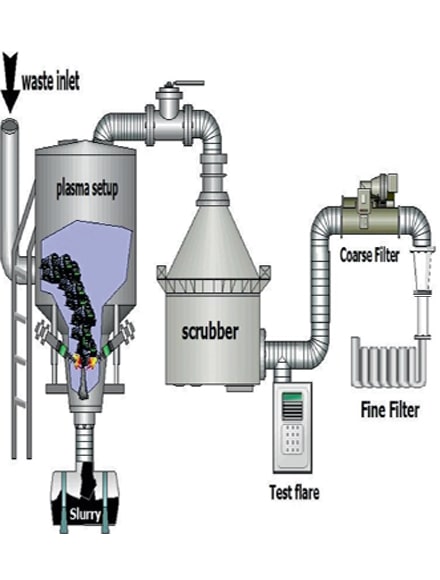
04
Convert waste to Plasma
Turning waste into plasma is one of the newest methods of energy production. In this method, wastes are converted into plasma at very high temperatures and the energy produced is converted into electricity. This method has many advantages over conventional waste burning and can help reduce pollution.
Using waste and turning it into plasma to produce energy is one of the most advanced methods of waste management. This process uses plasma technology to break down organic and inorganic materials into simpler gases.
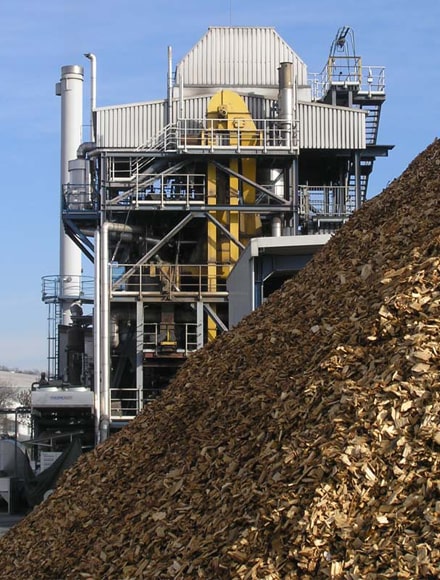

The main components of the waste disposal system with the help of plasma:
- Plasma reactor: where waste is decomposed under very high temperatures (up to 5000 degrees Celsius).
- Plasma source: An electric arc is usually used to produce plasma.
- Residue feeding system: Residues are continuously fed into the reactor.
- Gas purification system: The gases produced from the reactor are purified to remove impurities and pollutants.
- Energy production system: Refined gases are used as fuel to produce electricity or heat.
The stages of the waste removal process with the help of plasma:
- Separation and pretreatment: waste is collected and separated to separate non-combustible materials.
- Feeding to the reactor: The prepared wastes enter the plasma reactor.
- Decomposition in the reactor: wastes are decomposed under very high temperature and turn into simpler gases such as hydrogen (H2) and carbon monoxide.
Advantages of Plasma
- Reducing pollution: This method can help reduce air pollution.
- High energy production: converting waste into plasma can produce a lot of energy.
- Eliminating toxic substances: This method can completely eliminate toxic substances.
- Reducing air pollution and eliminating toxic substances completely.
- High energy production and reduction of waste disposal costs.
Disadvantages of Plasma
- High cost: the equipment required for this method is very expensive.
- Need for advanced technology: This method requires advanced and complex technologies.
- The need for proper management of residual waste and high energy consumption for plasma production.
- Very high costs for equipment and advanced technologies.
The United States is one of the leading countries in the use of waste-to-plasma technology. One of the successful examples of this technology is the waste-to-plasma plant in Florida, which can convert thousands of tons of waste into energy per day. Using very high temperatures, this power plant converts waste into plasma and converts the produced energy into electricity.
Using waste to produce energy not only helps to reduce environmental pollution but can also be used as a sustainable source of energy. Due to different types of waste and various methods of energy production, it is possible to achieve optimal management of waste and preservation of natural resources.
In the world, other methods are used to produce energy from waste, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. Of course, the use of each of these methods depends on management decisions and the type of waste. Some of these methods are:
Gasification
Gasification is a process in which wastes are converted into gas at high temperatures in the presence of a small amount of oxygen. This gas can be used as fuel to produce electricity and heat.
Advantages:
- Reducing the volume of waste: This method can significantly reduce the volume of waste.
- Clean energy production: The produced gas can be used as a clean fuel.
Disadvantages:
- High cost: The equipment required for gasification is very expensive.
- Need for advanced technology: This method requires advanced technologies.
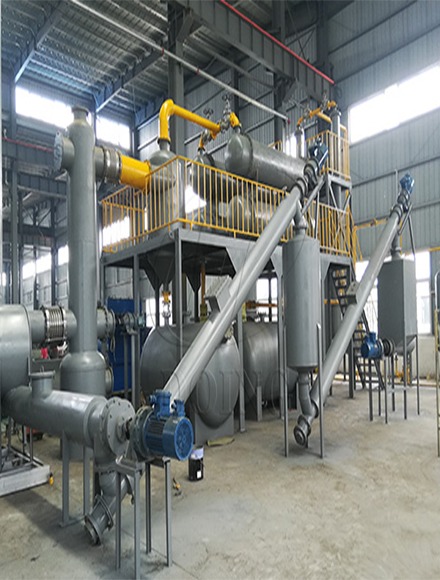
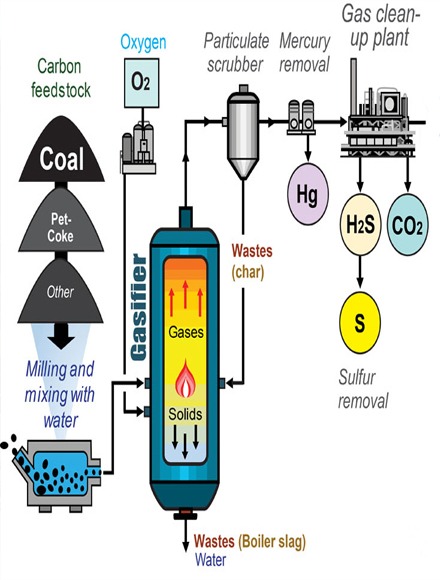

Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process in which wastes are decomposed in the absence of oxygen and at high temperatures. This process results in the production of gas, oil and solid carbon, each of which can be used as energy sources.
Advantages:
- Production of various products: This method can produce various products such as gas, oil and carbon.
- Reducing pollution: Pyrolysis can help reduce air pollution.
Disadvantages:
- High cost: Pyrolysis equipment and processes are expensive.
- Need for proper management: Produced products need proper management and processing.
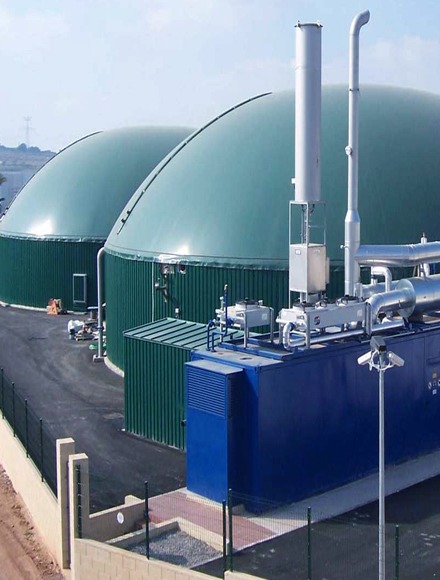
Anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a process in which organic wastes are decomposed under anaerobic conditions and biogas is produced. This gas can be used as fuel to produce electricity and heat.
Advantages:
- Use of organic waste: This method uses organic waste such as food and agricultural waste.
- Production of clean energy: the produced biogas can be used as a clean fuel.
Disadvantages:
- Need a lot of space: A lot of space is needed for anaerobic digestion.
- Time-consuming: The biogas production process may be time-consuming.
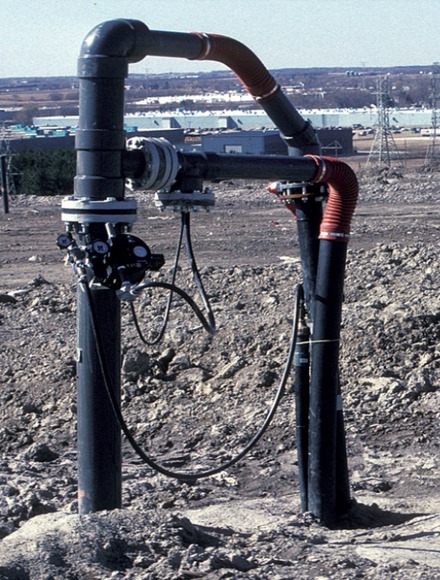


Gas Recovery from Landfills
Landfill gas recovery is a process in which gases produced from landfills are collected and used as fuel. These gases mainly include methane, which can be used as fuel to generate electricity and heat.
Advantages:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: This method can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Utilization of available resources: Landfill gases are generated naturally and can be used as an energy source.
Disadvantages:
- Need for collection equipment: Collection and processing of landfill gas requires special equipment.
- Variable gas quality: The quality of the produced gas may be variable and require further processing.